The solution is simple to recalculate the experience index at any time on Windows 8.1, or Windows 11 and 10!Content:
1.) ... Start recalculating the performance index!
|
| (Image-1) Recalculate the experience index in Windows! |
 |
The performance index is a number that can give approximately an idea of the performance of your computer or laptop. Your system is rated from one to 9.9 points on Windows 10 and at 7 to 7.9. The final result is displayed according to the weakest component.
| (Image-2) Recalculate the windows 10 experience index! |
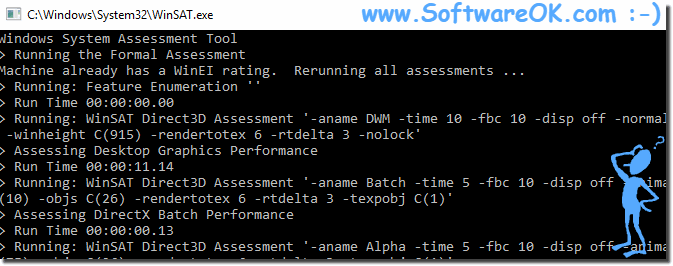 |
Many users wonder where the performance index was missing in Windows 10 because it was very convenient in the seven and other operating system versions to estimate the approximate performance of the system. Of course, one does not rely solely on this index, it is better to measure the gaming performance of the video card and other components of the system and to draw conclusions, in my opinion, the thing is very useful for the inexperienced user and also for experienced Widows user.
2.) The performance index is not calculated and not displayed Windows 10?!
The most important thing on Windows 11, 10 etc. is that all drivers are installed correctly, and that the hardware is well recognized, this should be checked beforehand otherwise the performance index will not be calculated correctly or will be aborted. Current drivers also bring better values in the Windows performance index, which is valid for all Windows Microsoft operating systems.
►►► Driver update via the Windows 10 device manager!
3.) More information about performance index on Windows 11 and 10!
The Windows Experience Index was/is a quick way for Windows users to find out the overall performance of their computer and the immediate bottlenecks. Microsoft has removed the graphics version of the Windows Experience Index in Windows. However, the underlying tool, the Windows System Assessment Tool, lives on. Better still, you can easily access the old performance ratings. This is how you can check your Windows Experience Index on Windows 11, 10, etc.
The Performance Index, also known as the Windows Experience Index, was first introduced in Windows Vista and continued in later versions such as Windows 7, Windows 8 and Windows 8.1. However, with Windows 10 and Windows 11, the performance index has been officially removed and is no longer available. The Windows Performance Index evaluates your computer's performance based on five main components:
Processor (CPU):
This review evaluated the speed and performance of your CPU.
Random Access Memory (RAM):
The amount and speed of your RAM was evaluated here.
Graphics (graphics card):
The graphics card was evaluated for its 2D and 3D graphics performance.
Graphics (game graphics):
This value specifically referred to the 3D graphics performance of your gaming graphics card.
Primary hard drive (hard drive subsystem):
The speed and performance of your hard drive or SSD have been evaluated here.
The results were given as numbers from 1.0 to 7.9 (in Windows 7) or from 1.0 to 9.9 (in Windows 8.1), with higher values indicating better performance.
In Windows 10 and Windows 11, the performance index has been removed because it is no longer considered a relevant method for evaluating a computer's performance. Instead, you can measure your computer's performance using tools like Task Manager or dedicated benchmark software solutions. These tools provide a more detailed and up-to-date analysis of your hardware and system performance.
If you need specific information about the performance of your Windows 10 or Windows 11 computer, you can open Task Manager by pressing Ctrl+Shift+Esc to get up-to-date information about CPU, RAM, and other resources.
4.) For me the performance index on Windows always stays the same, it doesn't get any better!
If all the usual measures to improve performance index are not effective, there are a few additional steps you can take:1. Check hardware:
Make sure your hardware is working properly. Check whether all components such as CPU, RAM, graphics card and hard drive are working properly. Check for possible defects or incompatibilities.
2. Update drivers:
Make sure all drivers for your hardware are up to date. Outdated or faulty drivers can affect performance. Check the manufacturer's website to download and install the latest drivers.
3. Optimize OS:
Perform thorough system optimization to ensure your OS runs efficiently. This can include disabling unnecessary background processes, deleting temporary files, and optimizing system settings.
4. Troubleshoot software conflicts:
Check whether certain programs or processes are affecting performance. Sometimes conflicts between different programs can cause performance problems. Identify and resolve such conflicts by uninstalling unnecessary programs or stopping processes that are consuming resources.
5. Upgrade hardware:
If your hardware is outdated and can no longer keep up with current demands, a hardware upgrade may be necessary. This may include replacing components such as CPU, RAM, or graphics card to improve overall performance.
6. Seek professional help:
If you continue to have difficulty improving your system's performance, it may be a good idea to seek professional help. An expert can perform a thorough diagnosis and recommend tailored solutions to your specific problems.
By following these steps, you can hopefully improve your system's performance, even if the usual measures aren't enough.
5.) Can the performance index become worse under Windows?
Yes, the performance index on Windows can indeed become worse. This can happen for various reasons:1. Hardware problems:
If a hardware component such as If the CPU, graphics card or hard drive is defective or not working properly, this can lead to a deterioration in the performance index. For example, overheating the CPU can cause it to work slower, thereby affecting the overall performance of the system.
2. Software problems:
Software conflicts, poorly optimized programs or malicious software can negatively affect the performance of your system and thus also worsen the performance index. Adding new software or updating drivers can also sometimes cause performance issues if they are not configured or installed properly.
3. Operating system problems:
Problems with the operating system itself can also lead to a deterioration in the performance index. These could be, for example, faulty system files, hard drive fragmentation, or registry problems.
4. System overload:
If the system is overloaded, for example by running multiple resource-intensive programs at the same time or due to a lack of available memory, this can lead to a deterioration in overall performance and performance index.
5. Hardware aging:
Over time, the performance of hardware components may decline due to wear and aging, which may also negatively impact the performance index.
It is important to identify the cause of performance index degradation in order to take appropriate action to resolve the issues and restore system performance. This may include checking hardware, troubleshooting software problems, or upgrading outdated hardware.
FAQ 3: Updated on: 8 April 2024 08:03
