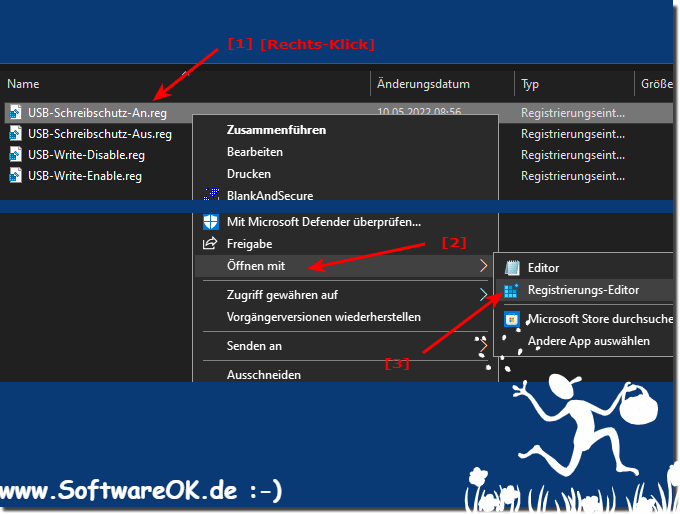
The registry hack to disable writing to USB drives is very popular to prevent unauthorized people from copying data to the stick!1.) ... Registry entry for write protection on external USB drives!
|
| (Image-1) Registry entry for write protection on external USB drives! |
 |
Info:
Once you use the registry hack, you need to restart Windows for the changes to take effect. (on Windows 11, 10, it is not required). Also note that you have administrator rights on the computer when doing this, this setting can be easily reset if you have admin rights.
Once you use the registry hack, you need to restart Windows for the changes to take effect. (on Windows 11, 10, it is not required). Also note that you have administrator rights on the computer when doing this, this setting can be easily reset if you have admin rights.
2.) Does this write protection work on MS Windows 11, 10 and new MS servers?
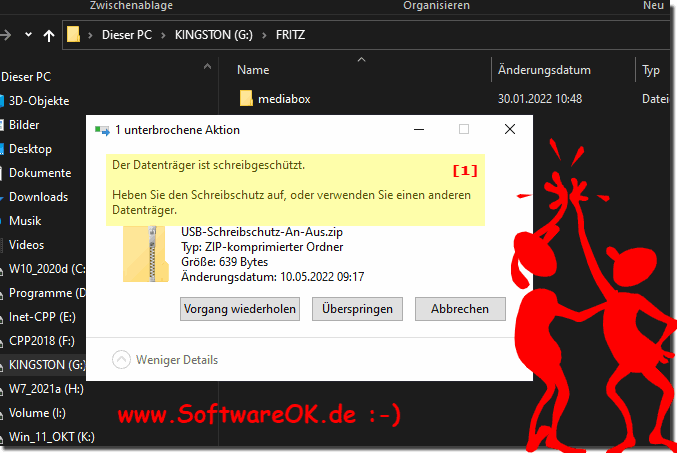
Yes the registry hack to disable writing to USB drives works on all MS Windows desktop and server operating systems!When trying to write to the USB stick, an error message appears and the data cannot be copied or transferred to the corresponding external USB medium
| (Image-2) Registry entry write protection on external USB drives! |
 |
3.) Additional information and recommendations on write protection etc.!
After applying the registry hack, in most cases you will need to restart Windows for the changes to take effect. However, this is often not necessary with Windows 10 and Windows 11. Note that you must have administrative rights on your computer to perform this procedure. The setting can be reset at any time as long as you have admin rights.Additional notes and recommendations;
- Security aspect:
Write protection is a simple and effective method to prevent unauthorized storage of data on external USB drives. This measure can be particularly useful in environments with high security requirements.
- Data backup:
Before making changes to the Windows registry, you should create a backup of your current registry settings in order to be able to quickly undo any potential problems.
- Write protection for specific devices:
It is also possible to activate write protection only for certain USB devices. To do this, you must manually add the hardware device path in the registry and specifically set the write protection.
4.) What does write protection affect and when is it useful?
Write protection on USB drives in Windows 11, Windows 10 and Windows Server has a variety of implications and can be useful or detrimental in different scenarios. Here is a detailed overview of what write protection affects:
Impact of write protection on Windows 11, 10 and Windows Server
1. Preventing data loss and manipulation
- Prevent unauthorized copying of data:
Write protection prevents users from copying data to the USB drive, protecting sensitive information from unauthorized access.
- Prevent data tampering:
Since data cannot be written to the drive, existing data on the USB drive cannot be modified or deleted. This is especially useful in environments where data integrity must be ensured.
2. System-wide impacts
- Write protection on all external USB drives:
The write protection applies system-wide to all USB drives connected to the computer. This means that no data can be written to any USB drive, regardless of which device is connected.
- Also applies to USB hard drives:
The write protection affects not only USB sticks, but also larger external USB hard drives, provided they are recognized as removable storage devices.
3. Software interaction
- Applications cannot make changes:
Applications that try to save or change data on USB drives will fail. This also applies to automatic backup programs or synchronization services that access USB drives.
- Software installation not possible:
If an application tries to install itself on a USB drive or save data to it, this will be prevented by the write protection.
4. Security aspects
- Malware protection:
Write protection can help prevent malware from trying to spread on USB drives. Malware cannot write data to a write-protected drive or modify existing files.
- Data encryption:
When using encrypted USB drives, the contents remain secure because no unencrypted data can be written to the drive.
5. Limited usability of USB drives
- Limited file management:
Users cannot create new files or folders, rename, move or delete existing files. All write operations are blocked by write protection.
- Backup and storage solutions:
USB drives can no longer be used as a destination for backup or storage solutions, which limits their use for data backups.
6. Operating system functions
- No temporary files:
The operating system or applications cannot create temporary files on the USB drive. This may affect the functionality of certain programs or operating system features that want to store temporary data on USB media.
- System crash dumps:
Windows cannot store crash dumps on a write-protected USB drive, which may be relevant for troubleshooting system crashes.
7. Compatibility and operating system support
- Supported by Windows versions:
Write protection works on Windows 11, Windows 10, and modern Windows Server versions. It remains in place even after system updates or upgrades, unless the corresponding registry entry is manually changed.
- Differences between operating systems:
While write protection works similarly on all mentioned operating systems in most cases, certain features or security policies might be handled differently depending on the version or configuration.
Limitations and possible problems
- Loss of write capability:
Write protection can cause unexpected problems when users or applications need write access to USB drives, for example for software updates, file transfers or backups.
- Administrative rights required:
Changes to the registry require administrative rights. Users without these rights cannot enable or disable write protection.
- No protection against physical theft:
While write protection prevents data from being copied, it does not provide protection against physical theft of the USB drive.
Conclusion
Write protection on USB drives is a powerful tool to ensure data security and integrity. It protects against unauthorized access and data loss, but it significantly limits the usability of USB drives and requires a careful consideration of the pros and cons, depending on the use case and security requirements.
FAQ 6: Updated on: 12 June 2024 06:13
