The security and glance in MS Windows 10 & 11, defender, account protection, is a overview about the security settings and rules in Windows!
Everyone knows how to restrict folder access to folders, or know Defender folder protection, but two separate stories are "security at a glance", brings users panic even more. Protection doubled, but apparently useful. However, it is much more sensible to use guest, admin and standard user accounts correctly!
1.) ... Opening “Security at a glance” on Windows 11, 10 and MS Server from 2019!
2.) ... Security, data, private on MS Windows desktop operating systems!
3.) ... Common security and privacy errors on MS Windows operating systems!
4.) ... Do other operating systems also have “security at a glance” like Windows?
1.) Opening “Security at a glance” on Windows 11, 10 and MS Server from 2019!
Right-click on the Defender icon of the Windows 10 Taskbar (Info / Notification/ Area). (Not Area 51), or start Windows 10 Run Dialog and Enter the command windowsdefender:
Please read this: ►►►► Security baseline for Windows 10 v1803!
►►► Security in 1803 W10 is the best ever Windows OS!
| Security and glance in Windows 10, defender, account protection! |
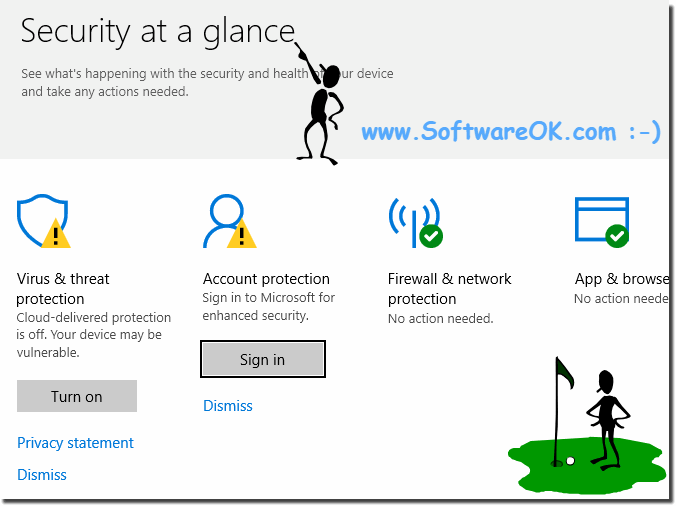 |
Microsoft is pleased to announce the draft release of the security configuration baseline settings for the upcoming Windows 10 version 1803, codenamed “Redstone 4.” Please evaluate this proposed baseline and send us your feedback via blog comments below.
►►►►► The security in Windows 10 18.03!
►►► MS says
Info:
As you can see in Windows 10 screenshot above, it is very easy to always keep an eye on the security on the computer under Windows. However, you can easily and fast use this example not only on Windows 10 Home, Enterprise and Pro, but also safely check the security aspects on previous versions such as Windows 8.1 Home and Pro.
Of course, this MS feature does not matter if it's a Windows desktop machine, a tablet-PC, Surface Pro / Go, or even a server operating system. It really makes a lot of sense to use this simple yet effective tool to check the safety of the system. It was successfully tested and verified on overseas MS.
As you can see in Windows 10 screenshot above, it is very easy to always keep an eye on the security on the computer under Windows. However, you can easily and fast use this example not only on Windows 10 Home, Enterprise and Pro, but also safely check the security aspects on previous versions such as Windows 8.1 Home and Pro.
Of course, this MS feature does not matter if it's a Windows desktop machine, a tablet-PC, Surface Pro / Go, or even a server operating system. It really makes a lot of sense to use this simple yet effective tool to check the safety of the system. It was successfully tested and verified on overseas MS.
2.) Security, data, private on MS Windows desktop operating systems!
►► Surf privately incognito or anonymously with Chrome!
►► MS Edge shortcut for private surfing under Windows 11!
►► Can you create a restore point under Windows 11?
►► Safely remove files using the ERASE command, examples?
►► Should I use MS Windows Recycle Bin or securely delete it immediately?
3.) Common Security and Privacy Mistakes on MS Windows Operating Systems!
Some common security and privacy errors on Microsoft Windows operating systems are:1. Unupdated software:
Neglecting software updates can leave security holes that can be exploited by attackers. Regular updates are crucial to close these gaps.
2. Weak passwords:
Using simple or easy-to-guess passwords leaves your accounts vulnerable to hacking. It is important to use strong passwords that consist of a combination of upper and lower case letters, numbers and special characters.
3. Disable Firewall:
Windows Firewall provides basic protection against unwanted network traffic. Disabling the firewall increases the risk of attacks and unwanted access to your system.
4. Lack of antivirus and anti-malware software:
Without a reliable antivirus and anti-malware solution, you are vulnerable to malicious software and viruses. It is important to install up-to-date security software and run regular scans.
5. Opening file attachments and links in emails from unknown senders:
Opening file attachments or clicking links in emails from unknown senders can lead to malware infections or phishing attacks. Be careful and always check the authenticity of emails before clicking on any links or attachments.
6. Lack of data backup:
Lack of regular data backup can lead to data loss, whether due to hardware failure, malware attacks or accidental file deletion. It is important to back up your important files regularly and ensure that these backups are current.
7. Use standard administrator privileges:
Using an account with administrator privileges for everyday tasks increases the risk of unwanted changes to the system and makes it more vulnerable to malware attacks. Instead, use a standard user account for everyday activities and grant administrative rights only when needed.
About:
By avoiding these common mistakes and implementing best security practices, you can significantly improve the security and privacy of your Windows operating systems.
By avoiding these common mistakes and implementing best security practices, you can significantly improve the security and privacy of your Windows operating systems.
4.) Do other operating systems also have “security at a glance” like Windows?
The “security at a glance” concept found on Windows operating systems is not directly transferable to other operating systems. Each operating system has its own security features and tools, but they have similar goals:to inform users about the security status of their system and to help them manage security aspects.
Here are some examples of security features or tools in other operating systems:
1. macOS (Apple):
macOS has the Security and Privacy system preference panel that allows users to set various security and privacy settings such as firewall, gatekeeper (for checking app downloads ) and data protection (to manage app access rights to personal data). It also offers a built-in malware protection feature called “XProtect”.
2. Linux:
Linux distributions offer different security features depending on the distribution and desktop environment. For example, Ubuntu has the Security and Privacy settings panel, which provides similar functionality such as firewall configuration and privacy settings management. Linux systems also often use package management systems such as APT (Advanced Package Tool) to provide security updates for installed software.
3. Android (Google):
Android, Google's operating system designed for mobile devices, offers security features such as Google Play Protect, which automatically scans apps for malware, and permission controls that allow users to limit apps' access to specific device resources to control .
4. iOS (Apple):
iOS, Apple's operating system for mobile devices such as iPhones and iPads, has security features such as the App Store, which reviews apps before publishing, and sandbox environments, which prevent apps from running in isolated environments Minimize security risks.
These examples show that other operating systems offer similar security features, but may not have a special feature called “Security at a Glance” like Windows does. Instead, security information and features are often provided through various system settings or applications.
